Astronomers Find the Evidence of Supernova Remnants
- News
- 2.4K
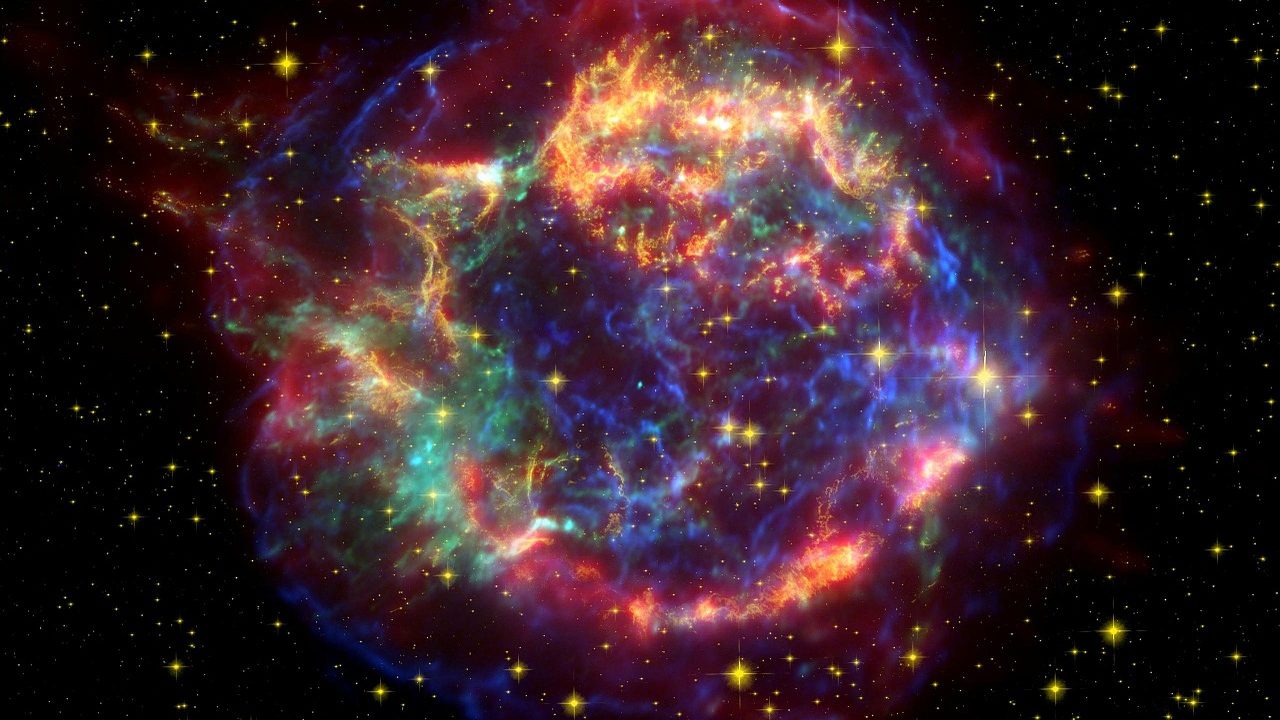
For several centuries, astronomers have been fascinated by large explosions that occur at the end of a star’s lifecycle, resulting in a phenomenon called a supernova. A team of Indian astronomers has found tell-tale evidence of a supernova explosion in a star-forming region called G351.7–1.2.
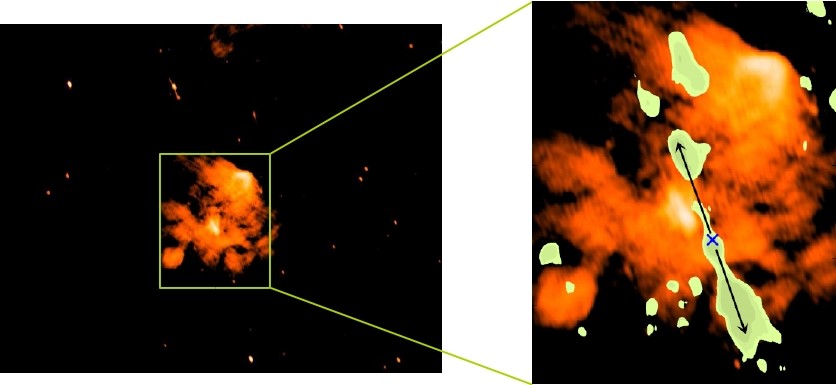
The evidence is in the form of a high-velocity jet of atomic hydrogen. The team consisted of scientists from Indian Institute of Space science and Technology (IIST), Thiruvananthapuram, Indian Institute of Science (IISc), Bengaluru and National Centre of Radio Astrophysics (NCRA), Pune.
The research team, led by V. S. Veena of IIST, found that the jet is in the direction of Scorpius constellation. The explosion should have resulted in a compact stellar object such as a neutron star or a pulsar or a black hole. However, there is no trace of either yet.
Massive stars with a mass more than 8-10 times that of our Sun end up as supernova explosions. The explosions brighten to intensity of million suns for a few days and then slowly fade into oblivion. The bursts throw up vast amounts of gas and particles at high velocity in all directions and they appear mostly circular (in many cases bubble-shaped) with hot filament-like structures.
The blasts rip off the outer layers of the dead star while the inner core collapses to become exotic stellar objects such as a neutron star, a pulsar or a black hole.
The group was probing the region G351.7–1.2 using the Giant Metrewave Radio Telescope (GMRT), operated by the National Centre of Radio Astrophysics in Pune. “We observed a large number of gas clouds and chanced upon a structure that appeared like a supernova remnant. It was bubble shaped, which is usual for a supernova remnant. Radio observations at different frequencies confirmed this view,” explained Veena.
“We found high-velocity jets of atomic hydrogen extending to about 20 light years racing at a speed of about 50 km per second in opposite directions in the neighbourhood. Clearly, there was a supernova explosion. However, despite our efforts, we could not find the leftover of the massive star,” observed Sarita Vig, a faculty member at IIST and a member of the study team.
The presence of highly directional jet points towards the presence of a compact object such as a black hole or a neutron star at the centre. “However, our efforts in finding it at low radio frequencies did not yield positive results,” added Nirupam Roy, another member of the team based at IISc.
The researchers have not given up hope. “It is possible that the object responsible for the jet is elusive at the observed radio wavelengths. Further studies in other regions of the electromagnetic spectrum may give more hints about the nature of the compact source that is responsible for the genesis of this jet within the supernova remnant”, says Jayanta Roy of NCRA and a collaborating member of the study.
Supernovae have a long history. Tycho Brahe, a European astronomer, chanced upon a ‘new star’, today called as ‘Tycho’s supernova’, way back in 1572, shining brighter than Venus, the brightest object in the night sky. Until it faded in 1574, the new star dazzled the naked eye.
Stunned, at its appearance, Tycho published a book ‘Concerning the Star, new and never before seen in the life or memory of anyone’. What Tycho observed was not the birth of a new star, ‘Nova’ in Latin, but the spectacular death of a massive star. The name stuck, and stellar explosions are called ‘Nova’.
The study team has published its results in the Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society (MNRAS) – Letters. (India Science Wire)
If you liked this article, then please subscribe to our YouTube Channel for the latest Science & Tech news. You can also find us on Twitter & Facebook.