The protein responsible for the accumulation of somatic mutations in multiple cancers is identified.
- Biology
- 2.1K
Researchers from Taiwan identify the protein responsible for the accumulation of somatic mutations in various cancers. The study conducted by Dr. Shen, Chen-Yang and his team at Institute of Biomedical Sciences, Academia Sinica, shows that the protein B-Myb–A3B contributes to DNA damage and could be targeted by inhibiting Epidermal Growth Factor receptor (EGFR).
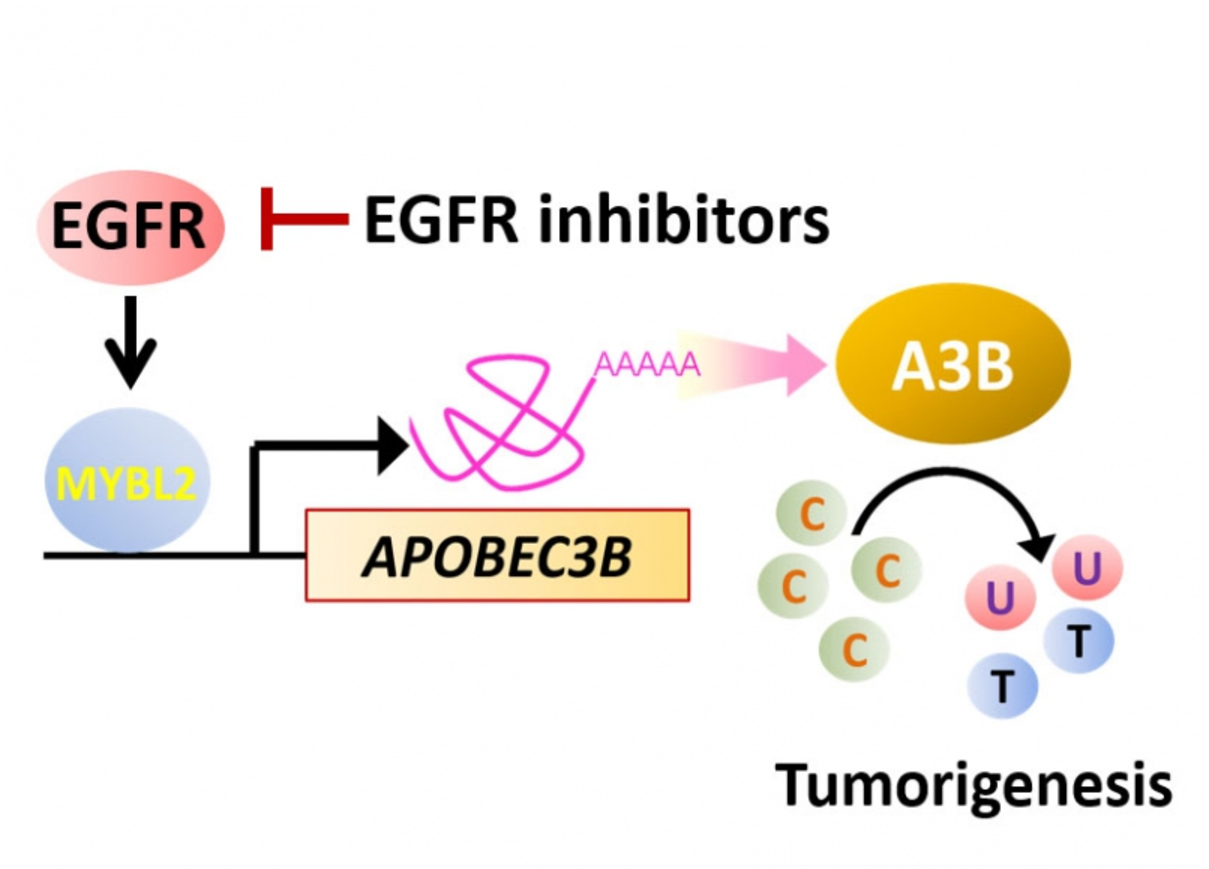
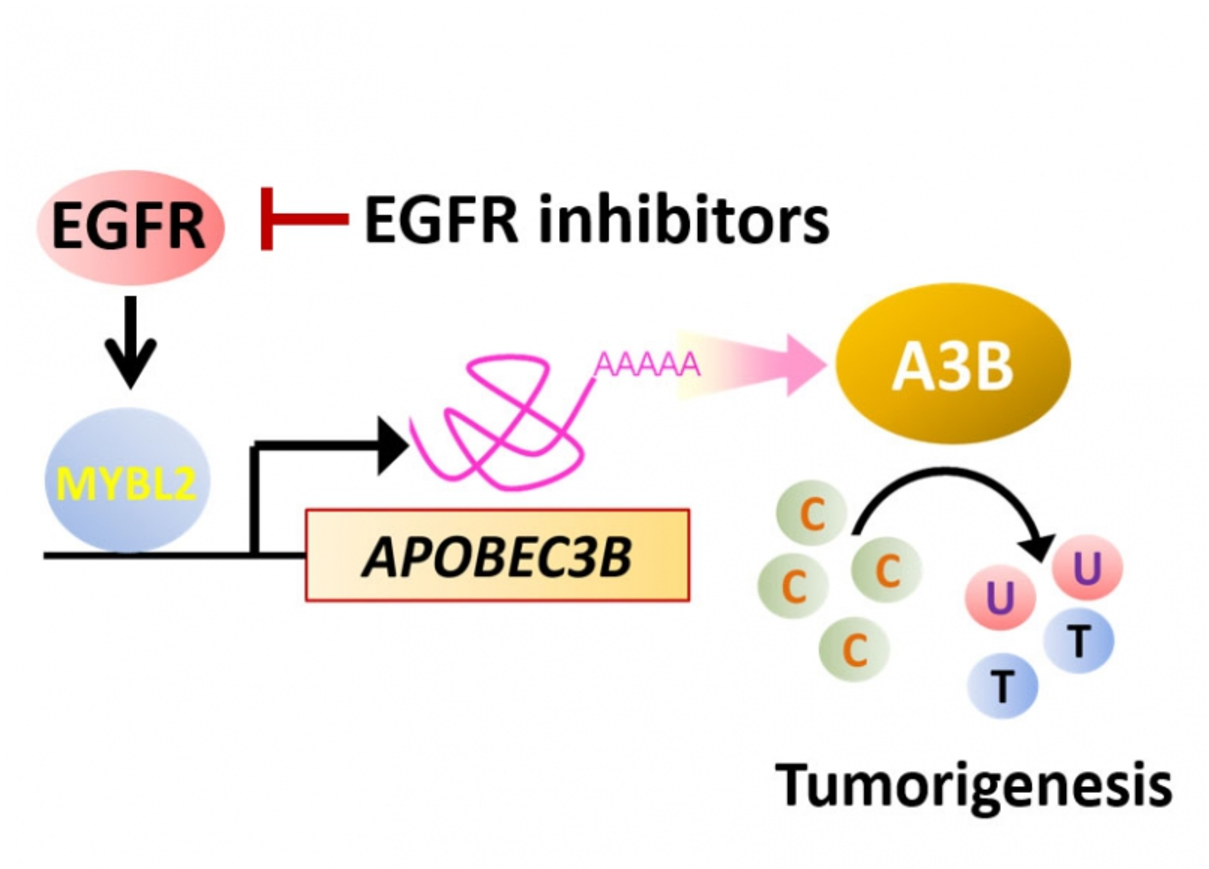
One of the key signatures of cancer genomes is the buildup of DNA mutations, the most abundant of which is the cytosine-to-thymine (C-to-T) transition that results from cytosine deamination. Investigation of The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) database has established that this changeover is triggered mainly by upregulation of the cytosine deaminase APOBEC3B (A3B), but the mechanism has not been completely characterized.
The research from the current study shows that B-Myb (coded by MYBL2 gene) binds the A3B promoter, causing transactivation, and this is responsible for the C-to-T transitions and DNA hypermutation in breast cancer cells. Analysis of TCGA database yielded similar results, supporting that MYBL2 and A3B are upregulated and putatively promote C-to-T transitions in multiple cancer types. Moreover, blockade of EGF receptor with afatinib attenuated B-Myb–A3B signaling, suggesting a clinically relevant means of suppressing mutagenesis.
The study suggests that the protein B-Myb–A3B contributes to DNA damage and could be targeted by inhibiting EGF receptor.
The full-length article can be found here https://www.nature.com/articles/srep44089



