New Center to Help Farmers Become Climate Resilient
- News
- 1.9K
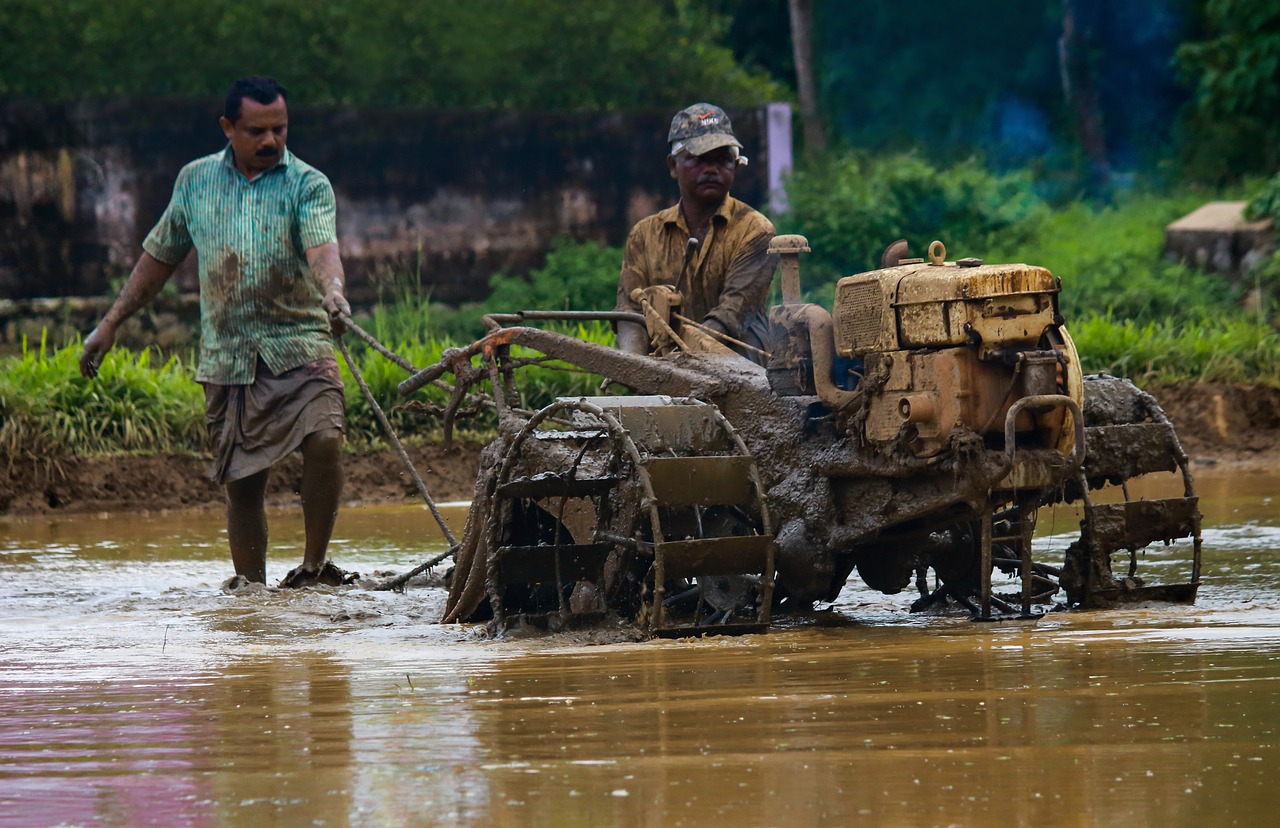
The Department of Science and Technology (DST) has established a center of excellence on climate change research for plant protection at the Hyderabad-based International Crop Research Institute for the Semi-Arid Tropics (ICRISAT). Its objective will be to help make agriculture more resilient to vagaries of climate change.
The center would focus on real-time structured surveillance for insect-pests and diseases using GPS-tagging techniques. It will also develop a model to for alert policymakers and farmers of any changes in the pattern of plant diseases and insect pests. In addition, it will work on the prediction of future climate scenarios and develop GIS-based risk maps for diseases and insect-pests at zonal, regional and State levels.
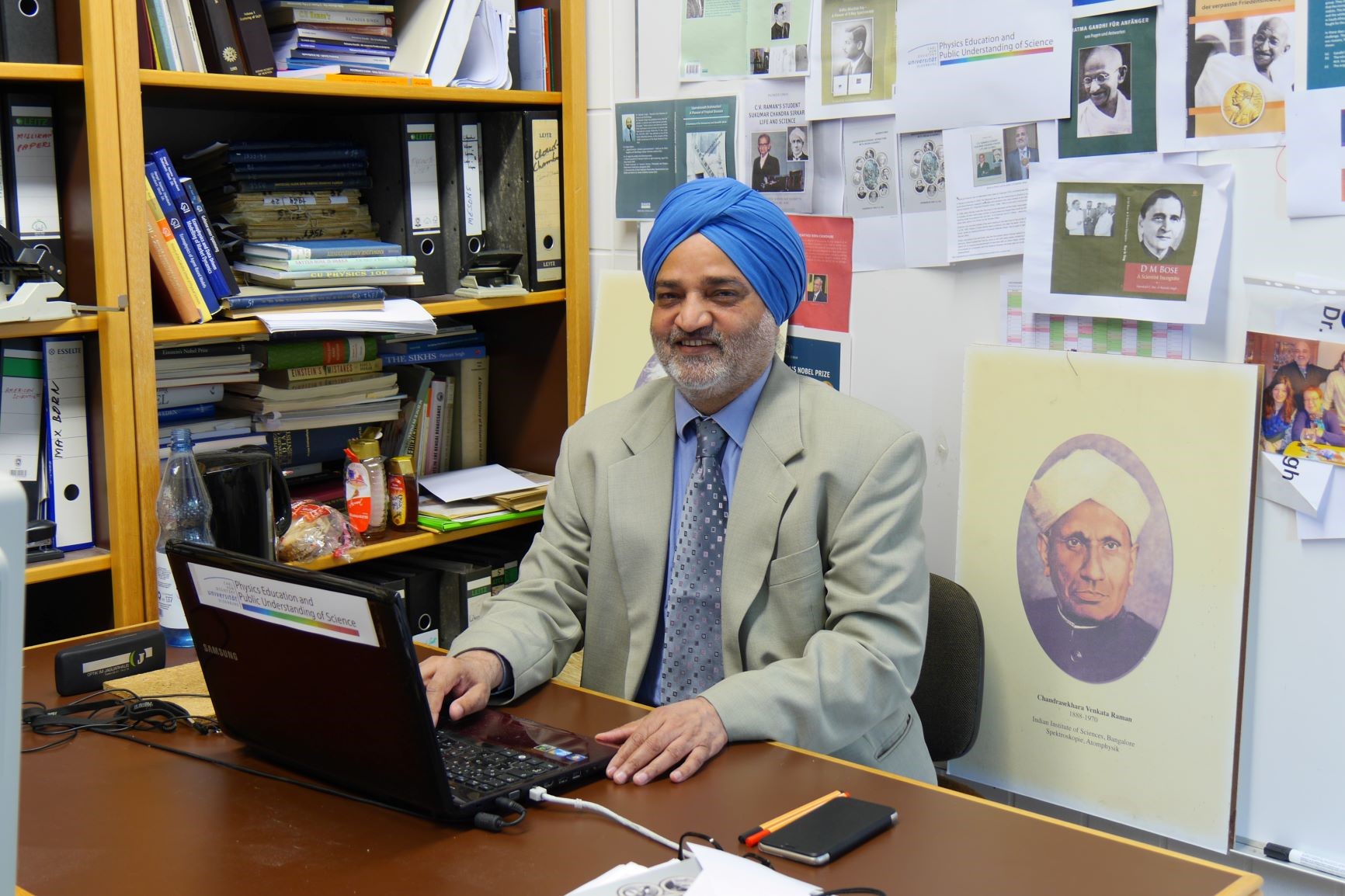
The center was formally launched by Dr. Akhilesh Gupta, Adviser and Head of the Climate Change Programme of DST.
“Providing advanced information and tools is important to strengthen the resilience of smallholder farmers,” said Dr. Peter Carberry, acting director general of ICRISAT.
“Research on changing patterns in plant diseases and insect-pests will induce shifts in the regional priority, strengthen location-specific crop breeding programmes under climate stress conditions and help us identify climate-smart and pest-resistant crop cultivars,” said Dr. P M Gaur, Research Programme Director-Asia at ICRISAT.
The Centre will operate as a consortium. Its partners include Indian Institute of Rice Research; University of Agricultural Sciences, Raichur; Indian Agricultural Research Institute; Punjab Agriculture University; Tamil Nadu Agricultural University; and centers of CGIAR, the global network of research institutions working in the area of agriculture.
Current estimates of climate change indicate possible increases in global mean annual temperatures in the order of 1 degree C by 2025 and 3 degrees C by 2100. Coupled with variability in rainfall pattern and an increase in global precipitation levels, this could result in new diseases and insect-pests, and increased risk of invasion by migrant diseases and insect pests.
Climate change, plant diseases, and insect-pests are estimated to cost an annual loss of USD 8.6 billion. (India Science Wire)
By Sunderarajan Padmanabhan
If you liked this article, then please subscribe to our YouTube Channel for the latest Science & Tech news. You can also find us on Twitter & Facebook.