Scientists Identify Potential Early Biomarker for Alzheimer’s
- News
- 1.8K
In a significant advance in the understanding of Alzheimer’s disease, scientists at the Indian Institute of Science (IISc), Bengaluru, have figured out the way memory deficit develops in early stages.
The researchers have found that early breaking down of a protein, fibrillar actin or F-actin, in the brain leads to disruption in communication among nerve cells and consequently memory deficits.

Prof. Vijayalakshmi Ravindranath
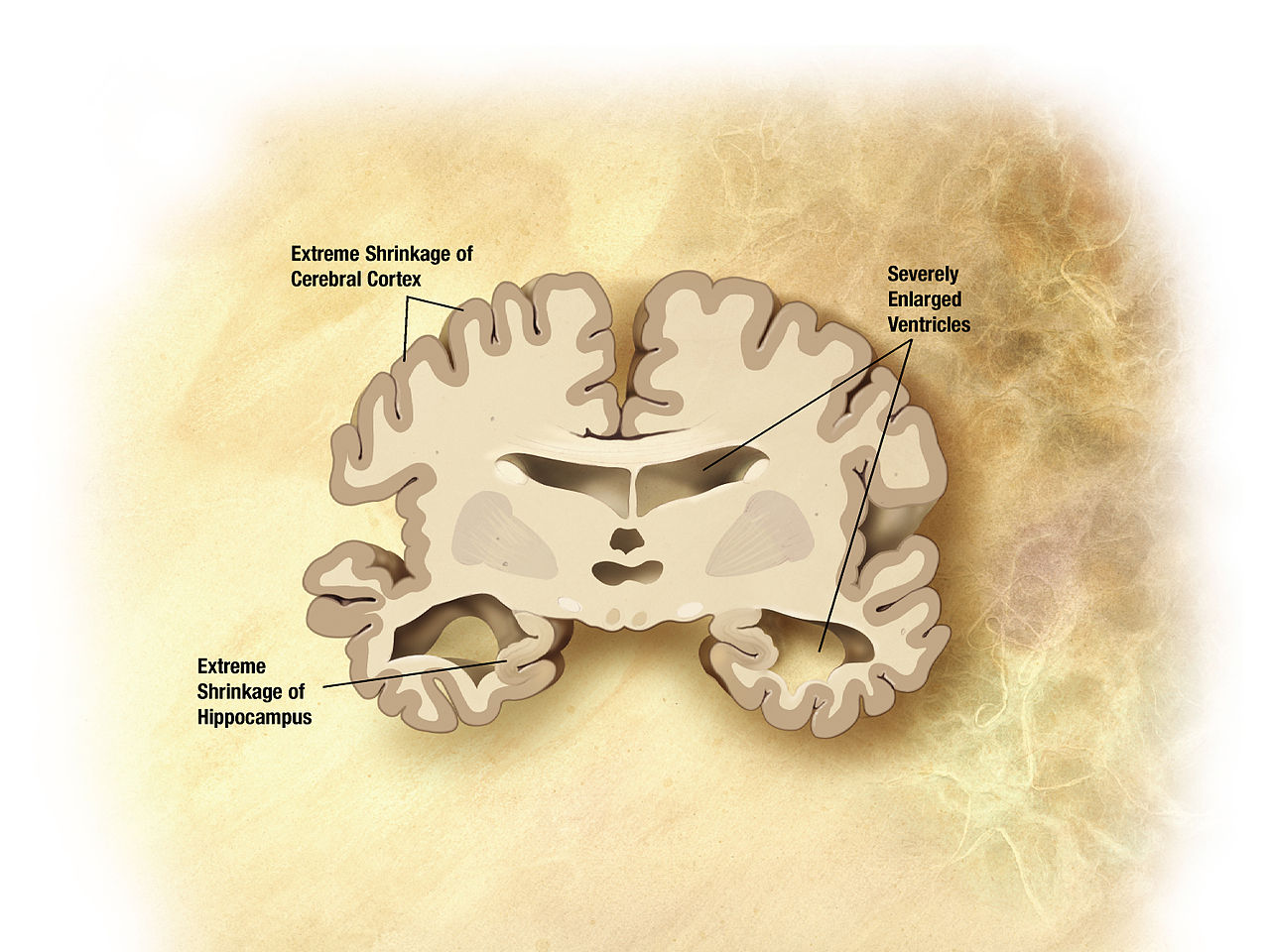
The protein is critical for maintaining the symmetry of mushroom-shaped projections called dendritic spines on the surface of nerve cells. These spines protrude into synapses – junctions between nerve cells – and act as docking spots for other neurons to connect and transmit signals. When synapses get disrupted due to loss of, or defects in dendritic spines, the flow of information between nerve cells is interrupted.
In the study, researchers used mice that were genetically modified to mimic Alzheimer’s disease to look at proteins involved in maintaining dendritic spine shape and number. F-actin proteins are found within these spines along with another related protein, G-actin. It was found that in mice with Alzheimer’s as young as one month old, F-actin/G-actin balance was disrupted, leading to lost spines. In contrast, the formation of toxic protein clumps called amyloid plaques – an early first clinical symptom of Alzheimer’s was seen when mice were 6 to 8 months old.
Further studies revealed that F-actin loss had an effect on the behavior of mice.
When researchers injected a chemical into affected mice that prevented F-actin from breaking down, they found that the mice were able to regain their normal behavior. “When we stabilized F-actin, we were able to see the behavior recovery,” pointed out Reddy Kommaddi, first author and DBT Ramalingaswami Fellow at the Centre for Neuroscience, IISc.
To test if similar effects were taking place in the human brain, researchers looked at post-mortem brain tissue samples of patients with Alzheimer’s disease, who had been studied for more than a decade before their death. The samples were obtained from collaborator David Bennett at the Rush Alzheimer’s Disease Center in Chicago, USA. Just like the mice with Alzheimer’s, these samples also showed a gradual breakdown of F-actin over time, as their symptoms — memory loss and accumulation of plaques — worsened.
“Because F-actin is a structural protein, it gives shape to all cells in the body and is present everywhere. It could potentially become a biomarker,” said Vijayalakshmi Ravindranath, senior author and Professor at the Centre for Neuroscience.
The research team included Reddy Peera Kommaddi, Debajyoti Das, Smitha Karunakaran, Siddharth Nanguneri, Deepti Bapat, Ajit Ray, Eisha Shaw, David A. Bennett, Deepak Nair and Vijayalakshmi Ravindranath. The study results have been published in the Journal of Neuroscience.
By Jyoti Singh
Journal Article
For the latest Science and Tech news and conversations, follow Research Stash on Twitter, Facebook, and subscribe to our YouTube channel